Products Category
- FM Transmitter
- 0-50w 50w-1000w 2kw-10kw 10kw+
- TV Transmitter
- 0-50w 50-1kw 2kw-10kw
- FM Antenna
- TV Antenna
- Antenna Accessory
- Cable Connector Power Splitter Dummy Load
- RF Transistor
- Power Supply
- Audio Equipments
- DTV Front End Equipment
- Link System
- STL system Microwave Link system
- FM Radio
- Power Meter
- Other Products
- Special for Coronavirus
Products Tags
Fmuser Sites
- es.fmuser.net
- it.fmuser.net
- fr.fmuser.net
- de.fmuser.net
- af.fmuser.net ->Afrikaans
- sq.fmuser.net ->Albanian
- ar.fmuser.net ->Arabic
- hy.fmuser.net ->Armenian
- az.fmuser.net ->Azerbaijani
- eu.fmuser.net ->Basque
- be.fmuser.net ->Belarusian
- bg.fmuser.net ->Bulgarian
- ca.fmuser.net ->Catalan
- zh-CN.fmuser.net ->Chinese (Simplified)
- zh-TW.fmuser.net ->Chinese (Traditional)
- hr.fmuser.net ->Croatian
- cs.fmuser.net ->Czech
- da.fmuser.net ->Danish
- nl.fmuser.net ->Dutch
- et.fmuser.net ->Estonian
- tl.fmuser.net ->Filipino
- fi.fmuser.net ->Finnish
- fr.fmuser.net ->French
- gl.fmuser.net ->Galician
- ka.fmuser.net ->Georgian
- de.fmuser.net ->German
- el.fmuser.net ->Greek
- ht.fmuser.net ->Haitian Creole
- iw.fmuser.net ->Hebrew
- hi.fmuser.net ->Hindi
- hu.fmuser.net ->Hungarian
- is.fmuser.net ->Icelandic
- id.fmuser.net ->Indonesian
- ga.fmuser.net ->Irish
- it.fmuser.net ->Italian
- ja.fmuser.net ->Japanese
- ko.fmuser.net ->Korean
- lv.fmuser.net ->Latvian
- lt.fmuser.net ->Lithuanian
- mk.fmuser.net ->Macedonian
- ms.fmuser.net ->Malay
- mt.fmuser.net ->Maltese
- no.fmuser.net ->Norwegian
- fa.fmuser.net ->Persian
- pl.fmuser.net ->Polish
- pt.fmuser.net ->Portuguese
- ro.fmuser.net ->Romanian
- ru.fmuser.net ->Russian
- sr.fmuser.net ->Serbian
- sk.fmuser.net ->Slovak
- sl.fmuser.net ->Slovenian
- es.fmuser.net ->Spanish
- sw.fmuser.net ->Swahili
- sv.fmuser.net ->Swedish
- th.fmuser.net ->Thai
- tr.fmuser.net ->Turkish
- uk.fmuser.net ->Ukrainian
- ur.fmuser.net ->Urdu
- vi.fmuser.net ->Vietnamese
- cy.fmuser.net ->Welsh
- yi.fmuser.net ->Yiddish
How to Design Pulse Amplitude Modulation?
Before we go into the design of pulse amplitude modulation let us know about the concept of modulation and different types of modulations.
What is Modulation?
Modulation is a process of changing the characteristics of a carrier signal like amplitude, frequency and width, etc. It is the process of adding information to the carrier signal. A carrier signal is a steady waveform with constant amplitude and frequency.
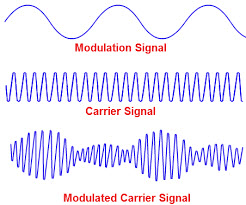
Modulation is normally applied to electromagnetic signals like radio laser and optical signals. The Audio, video, images and text data are added to the carrier signal for transmission over telecommunication.
Types of Modulation
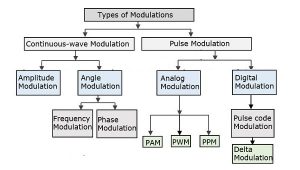
Modulation is categorized into two types depending on the type of signal.
* Continuous-wave Modulation
* Pulse Modulation
Continuous-wave modulation and Pulse modulation are further categorized as shown below.
Continuous-wave Modulation
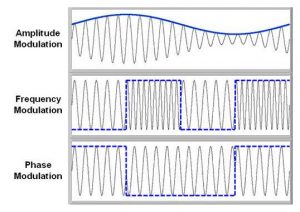
In continuous wave modulation signal is used as a carrier signal which modulates the message signal. There are three parameters that can be altered to achieve modulation namely, frequency, amplitude and phase. Thus, there are three types of modulations.
1. Amplitude Modulation
2. Frequency Modulation
3. Phase Modulation
Pulse Modulation
Pulse modulation is a technique in which the signal is transmitted with the information by pulses. This is divided into Analog Pulse Modulation and Digital Pulse Modulation.
Analog pulse modulation is classified as
* Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM)
* Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
* Pulse Position Modulation (PPM)
Digital modulation is classified as
* Pulse Code Modulation
* Delta Modulation
Pulse Amplitude Modulation
Pulse amplitude modulation is a technique in which the amplitude of each pulse is controlled by the instantaneous amplitude of the modulation signal. It is a modulation system in which the signal is sampled at regular intervals and each sample is made proportional to the amplitude of the signal at the instant of sampling. This technique transmits the data by encoding in the amplitude of a series of signal pulses.
There are two types of sampling techniques for transmitting a signal using PAM. They are:
* Flat Top PAM
* Natural PAM
Flat Top PAM: The amplitude of each pulse is directly proportional to modulating signal amplitude at the time of pulse occurrence. The amplitude of the signal cannot be changed with respect to the analog signal to be sampled. The tops of the amplitude remain flat.
Natural PAM: The amplitude of each pulse is directly proportional to modulating signal amplitude at the time of pulse occurrence. Then follows the amplitude of the pulse for the rest of the half cycle.
What is Modulation? Different Types of Modulation Techniques
Different Modulation Types & Techniques
Modulation Techniques Overview