Products Category
- FM Transmitter
- 0-50w 50w-1000w 2kw-10kw 10kw+
- TV Transmitter
- 0-50w 50-1kw 2kw-10kw
- FM Antenna
- TV Antenna
- Antenna Accessory
- Cable Connector Power Splitter Dummy Load
- RF Transistor
- Power Supply
- Audio Equipments
- DTV Front End Equipment
- Link System
- STL system Microwave Link system
- FM Radio
- Power Meter
- Other Products
- Special for Coronavirus
Products Tags
Fmuser Sites
- es.fmuser.net
- it.fmuser.net
- fr.fmuser.net
- de.fmuser.net
- af.fmuser.net ->Afrikaans
- sq.fmuser.net ->Albanian
- ar.fmuser.net ->Arabic
- hy.fmuser.net ->Armenian
- az.fmuser.net ->Azerbaijani
- eu.fmuser.net ->Basque
- be.fmuser.net ->Belarusian
- bg.fmuser.net ->Bulgarian
- ca.fmuser.net ->Catalan
- zh-CN.fmuser.net ->Chinese (Simplified)
- zh-TW.fmuser.net ->Chinese (Traditional)
- hr.fmuser.net ->Croatian
- cs.fmuser.net ->Czech
- da.fmuser.net ->Danish
- nl.fmuser.net ->Dutch
- et.fmuser.net ->Estonian
- tl.fmuser.net ->Filipino
- fi.fmuser.net ->Finnish
- fr.fmuser.net ->French
- gl.fmuser.net ->Galician
- ka.fmuser.net ->Georgian
- de.fmuser.net ->German
- el.fmuser.net ->Greek
- ht.fmuser.net ->Haitian Creole
- iw.fmuser.net ->Hebrew
- hi.fmuser.net ->Hindi
- hu.fmuser.net ->Hungarian
- is.fmuser.net ->Icelandic
- id.fmuser.net ->Indonesian
- ga.fmuser.net ->Irish
- it.fmuser.net ->Italian
- ja.fmuser.net ->Japanese
- ko.fmuser.net ->Korean
- lv.fmuser.net ->Latvian
- lt.fmuser.net ->Lithuanian
- mk.fmuser.net ->Macedonian
- ms.fmuser.net ->Malay
- mt.fmuser.net ->Maltese
- no.fmuser.net ->Norwegian
- fa.fmuser.net ->Persian
- pl.fmuser.net ->Polish
- pt.fmuser.net ->Portuguese
- ro.fmuser.net ->Romanian
- ru.fmuser.net ->Russian
- sr.fmuser.net ->Serbian
- sk.fmuser.net ->Slovak
- sl.fmuser.net ->Slovenian
- es.fmuser.net ->Spanish
- sw.fmuser.net ->Swahili
- sv.fmuser.net ->Swedish
- th.fmuser.net ->Thai
- tr.fmuser.net ->Turkish
- uk.fmuser.net ->Ukrainian
- ur.fmuser.net ->Urdu
- vi.fmuser.net ->Vietnamese
- cy.fmuser.net ->Welsh
- yi.fmuser.net ->Yiddish
Types of radio emissions F3E,F2D etc.
The International Telecommunication Union uses an internationally agreed system for classifying radio frequency signals. Each type of radio emission is classified according to its bandwidth, method of modulation, nature of the modulating signal, and type of information transmitted on the carrier signal. It is based on characteristics of the signal, not on the transmitter used.
An emission designation is of the form BBBB 123 45, where BBBB is the bandwidth of the signal, 1 is a letter indicating the type of modulation used of the main carrier (not including any subcarriers which is why FM stereo is F8E and not D8E), 2 is a digit representing the type of modulating signal again of the main carrier, 3 is a letter corresponding to the type of information transmitted, 4 is a letter indicating the practical details of the transmitted information, and 5 is a letter that represents the method of multiplexing. The 4 and 5 fields are optional.
This designation system was agreed at the 1979 World Administrative Radio Conference (WARC 79), and gave rise to the Radio Regulations that came into force on 1 January 1982. A similar designation system had been in use under prior Radio Regulations.
Designation details
Type of modulation

Type of modulating signal

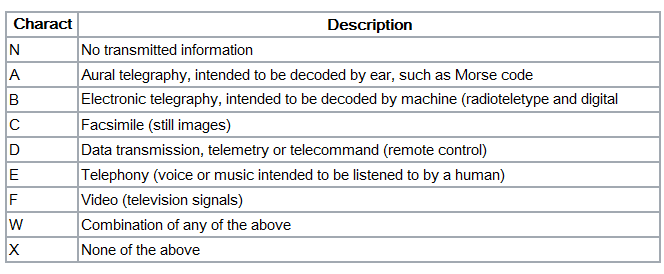
Type of transmitted information
Common examples:
Broadcasting
A3E or A3E G
Ordinary amplitude modulation used for low frequency and medium frequency AM broadcasting
F8E, F8E H
FM broadcasting for radio transmissions on VHF, and as the audio component of analogue television transmissions. Since there are generally pilot tones (subcarriers) for stereo and RDS the designator '8' is used, to indicate multiple signals.
C3F, C3F N
Analogue PAL, SÉCAM, or NTSC television video signals (formerly type A5C, until 1982)
C7W
ATSC digital television, commonly on VHF or UHF
G7W
DVB-T, ISDB-T, or DTMB digital television, commonly on VHF or UHF
Two-way radio
A3E
AM speech communication – used for aeronautical communications
F3E
FM speech communication – often used for marine radio and many other VHF communications
20K0 F3E
Wide FM, 20.0 kHz width, ±5 kHz deviation, still widely used for Ham Radio, NOAA weather radio, marine, and aviation users and land mobile users below 50 MHz [1]
11K2 F3E
Narrow FM, 11.25 kHz bandwidth, ±2.5 kHz deviation – All Part 90 Land Mobile Radio Service (LMRS) users operating above 50 MHz were required to upgrade to narrowband equipment by 2013-01-01. [2] [3] [4]
6K00 F3E
Even Narrower FM, future roadmap for Land Mobile Radio Service (LMRS), already required on 700 MHz public safety band
J3E
SSB speech communication, used on HF bands by marine, aeronautical and amateur users
R3E
SSB with reduced carrier (AME) speech communication, primarily used on HF bands by the military (a.k.a. compatible sideband)
Low-speed data
N0N
Continuous, unmodulated carrier, formerly common for radio direction finding (RDF) in marine and aeronautical navigation.
A1A
Signalling by keying the carrier directly, a.k.a. Continuous Wave (CW) or On-Off Keying (OOK), currently used in amateur radio. This is often but not necessarily Morse code.
A2A
Signalling by transmitting a modulated tone with a carrier, so that it can easily be heard using an ordinary AM receiver. It was formerly widely used for station identification of non-directional beacons, usually but not exclusively Morse code (an example of a modulated continuous wave, as opposed to A1A, above).
F1B
Frequency-shift keying (FSK) telegraphy, such as RTTY.[a]
F1C
High frequency Radiofax
F2D
Data transmission by frequency modulation of a radio frequency carrier with an audio frequency FSK subcarrier. Often called AFSK/FM.
J2B
Phase-shift keying such as PSK31 (BPSK31)
There is some overlap in signal types, so a transmission might legitimately be described by two or more designators. In such cases, there is usually a preferred conventional designator.