Products Category
- FM Transmitter
- 0-50w 50w-1000w 2kw-10kw 10kw+
- TV Transmitter
- 0-50w 50-1kw 2kw-10kw
- FM Antenna
- TV Antenna
- Antenna Accessory
- Cable Connector Power Splitter Dummy Load
- RF Transistor
- Power Supply
- Audio Equipments
- DTV Front End Equipment
- Link System
- STL system Microwave Link system
- FM Radio
- Power Meter
- Other Products
- Special for Coronavirus
Products Tags
Fmuser Sites
- es.fmuser.net
- it.fmuser.net
- fr.fmuser.net
- de.fmuser.net
- af.fmuser.net ->Afrikaans
- sq.fmuser.net ->Albanian
- ar.fmuser.net ->Arabic
- hy.fmuser.net ->Armenian
- az.fmuser.net ->Azerbaijani
- eu.fmuser.net ->Basque
- be.fmuser.net ->Belarusian
- bg.fmuser.net ->Bulgarian
- ca.fmuser.net ->Catalan
- zh-CN.fmuser.net ->Chinese (Simplified)
- zh-TW.fmuser.net ->Chinese (Traditional)
- hr.fmuser.net ->Croatian
- cs.fmuser.net ->Czech
- da.fmuser.net ->Danish
- nl.fmuser.net ->Dutch
- et.fmuser.net ->Estonian
- tl.fmuser.net ->Filipino
- fi.fmuser.net ->Finnish
- fr.fmuser.net ->French
- gl.fmuser.net ->Galician
- ka.fmuser.net ->Georgian
- de.fmuser.net ->German
- el.fmuser.net ->Greek
- ht.fmuser.net ->Haitian Creole
- iw.fmuser.net ->Hebrew
- hi.fmuser.net ->Hindi
- hu.fmuser.net ->Hungarian
- is.fmuser.net ->Icelandic
- id.fmuser.net ->Indonesian
- ga.fmuser.net ->Irish
- it.fmuser.net ->Italian
- ja.fmuser.net ->Japanese
- ko.fmuser.net ->Korean
- lv.fmuser.net ->Latvian
- lt.fmuser.net ->Lithuanian
- mk.fmuser.net ->Macedonian
- ms.fmuser.net ->Malay
- mt.fmuser.net ->Maltese
- no.fmuser.net ->Norwegian
- fa.fmuser.net ->Persian
- pl.fmuser.net ->Polish
- pt.fmuser.net ->Portuguese
- ro.fmuser.net ->Romanian
- ru.fmuser.net ->Russian
- sr.fmuser.net ->Serbian
- sk.fmuser.net ->Slovak
- sl.fmuser.net ->Slovenian
- es.fmuser.net ->Spanish
- sw.fmuser.net ->Swahili
- sv.fmuser.net ->Swedish
- th.fmuser.net ->Thai
- tr.fmuser.net ->Turkish
- uk.fmuser.net ->Ukrainian
- ur.fmuser.net ->Urdu
- vi.fmuser.net ->Vietnamese
- cy.fmuser.net ->Welsh
- yi.fmuser.net ->Yiddish
What is Modulation
Modulation is usually applied to electromagnetic signals -- radio, lasers/optics and computer networks. Modulation can even be applied to direct current (which can be treated as a degenerate carrier wave with amplitude 0 and frequency 0) mainly by turning it on and off (as in Morse code telegraphy), or applied to alternating current (as with power-line networking).
Common modulation methods include the following:
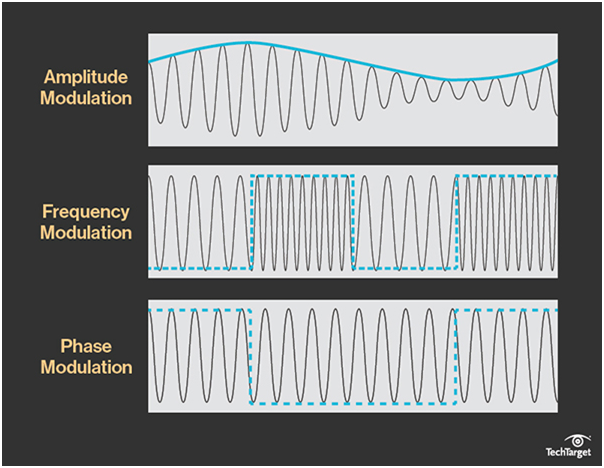
Amplitude modulation (AM), in which the height (i.e., the strength or intensity) of the signal carrier is varied to represent the data being added to the signal.
Frequency modulation (FM), in which the frequency of the carrier waveform is varied to reflect the frequency of the data.
Phase modulation (PM), in which the frequency of the carrier waveform is varied to reflect changes in the frequency of the data (similar but not the same as FM).
Polarization modulation, in which the angle of rotation of an optical carrier signal is varied to reflect transmitted data.
Pulse-code modulation, in which an analog signal is sampled to derive a data stream that is used to modulate a digital carrier signal.
More complex forms of modulation include phase-shift keying (PSK) and Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM). A computer modem allows a computer to connect to another computer or to a data network over a regular analog phone line by using the data signal to modulate an analog audio tone. A modem at the far end demodulates the audio signal to recover the data stream. A cable modem uses network data to modulate the cable service carrier signal.
Sometimes a carrier signal can carry more than one modulating information stream. A process called multiplexing combines the streams onto a single carrier -- e.g., by encoding a fixed-duration segment of one, then of the next, for example, cycling through all channels before returning to the first, a process called time-division multiplexing (TDM).