Products Category
- FM Transmitter
- 0-50w 50w-1000w 2kw-10kw 10kw+
- TV Transmitter
- 0-50w 50-1kw 2kw-10kw
- FM Antenna
- TV Antenna
- Antenna Accessory
- Cable Connector Power Splitter Dummy Load
- RF Transistor
- Power Supply
- Audio Equipments
- DTV Front End Equipment
- Link System
- STL system Microwave Link system
- FM Radio
- Power Meter
- Other Products
- Special for Coronavirus
Products Tags
Fmuser Sites
- es.fmuser.net
- it.fmuser.net
- fr.fmuser.net
- de.fmuser.net
- af.fmuser.net ->Afrikaans
- sq.fmuser.net ->Albanian
- ar.fmuser.net ->Arabic
- hy.fmuser.net ->Armenian
- az.fmuser.net ->Azerbaijani
- eu.fmuser.net ->Basque
- be.fmuser.net ->Belarusian
- bg.fmuser.net ->Bulgarian
- ca.fmuser.net ->Catalan
- zh-CN.fmuser.net ->Chinese (Simplified)
- zh-TW.fmuser.net ->Chinese (Traditional)
- hr.fmuser.net ->Croatian
- cs.fmuser.net ->Czech
- da.fmuser.net ->Danish
- nl.fmuser.net ->Dutch
- et.fmuser.net ->Estonian
- tl.fmuser.net ->Filipino
- fi.fmuser.net ->Finnish
- fr.fmuser.net ->French
- gl.fmuser.net ->Galician
- ka.fmuser.net ->Georgian
- de.fmuser.net ->German
- el.fmuser.net ->Greek
- ht.fmuser.net ->Haitian Creole
- iw.fmuser.net ->Hebrew
- hi.fmuser.net ->Hindi
- hu.fmuser.net ->Hungarian
- is.fmuser.net ->Icelandic
- id.fmuser.net ->Indonesian
- ga.fmuser.net ->Irish
- it.fmuser.net ->Italian
- ja.fmuser.net ->Japanese
- ko.fmuser.net ->Korean
- lv.fmuser.net ->Latvian
- lt.fmuser.net ->Lithuanian
- mk.fmuser.net ->Macedonian
- ms.fmuser.net ->Malay
- mt.fmuser.net ->Maltese
- no.fmuser.net ->Norwegian
- fa.fmuser.net ->Persian
- pl.fmuser.net ->Polish
- pt.fmuser.net ->Portuguese
- ro.fmuser.net ->Romanian
- ru.fmuser.net ->Russian
- sr.fmuser.net ->Serbian
- sk.fmuser.net ->Slovak
- sl.fmuser.net ->Slovenian
- es.fmuser.net ->Spanish
- sw.fmuser.net ->Swahili
- sv.fmuser.net ->Swedish
- th.fmuser.net ->Thai
- tr.fmuser.net ->Turkish
- uk.fmuser.net ->Ukrainian
- ur.fmuser.net ->Urdu
- vi.fmuser.net ->Vietnamese
- cy.fmuser.net ->Welsh
- yi.fmuser.net ->Yiddish
What Does Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) Refer To?
Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) is the name of a series of digital modulation methods and related analog modulation methods that are widely used to transmit information in modern telecommunications. It uses Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) digital modulation scheme or Amplitude Modulation (AM) analog modulation scheme to transmit two analog message signals or two digital bit streams by changing (modulating) the amplitude of two carriers. Two carriers of the same frequency are 90° out of phase with each other. This condition is called quadrature. The transmitted signal is generated by adding two carrier waves, has a certain amplitude resulting from the sum of both signals and a phase which again is dependent upon the sum of the signals. This method helps to double its effective bandwidth. QAM is also used with pulse AM (PAM) in digital systems such as wireless applications.
If the amplitude of one of the signals is adjusted then this affects both the phase and amplitude of the overall signal, the phase tending towards that of the signal with the higher amplitude content. At the receiver, due to their orthogonality, the two waves can be coherently separated (demodulated). Another key feature is that the modulation is a low-frequency/low-bandwidth waveform compared to the carrier frequency. This is called the narrowband assumption.Phase modulation (analog PM) and phase shift keying (digital PSK) can be seen as a special case of QAM, where the amplitude of the transmitted signal is a constant, but its phase is changing. This can also be extended to frequency modulation (FM) and frequency shift keying (FSK), as they can be regarded as special cases of phase modulation.
Now that we know that digital messager can be modulated to the RF Carrier by QPSK and BPSK.Why could not we combine then so as to get more digital information in the sine wave?That comes QAM,which is for short for QPSK & AM.In theory, QAM can be modulated with a smaller phase shift. There are more than two possible amplitudes to fill in each sine wave with more information. Usually the application is limited to the cable, because the noise there has been greatly attenuated.Fundamentally, QAM enables analog signals to effectively transmit digital information. It also provides a means for operators to transmit more bits in the same time period, effectively increasing bandwidth.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using QAM?
Efficient usage of bandwidth is the major benefit of QAM modulation deviations. This is due to the fact that QAM symbolize more number of bits per carrier. For example, 256-QAM maps 8 bits per carrier, and 16-QAM maps 4 bits per carrier.Disadvantages are, QAM modulation process is more prehensile to the noise.This is because the transmission states are very close, requiring a lower noise level to move the signal from one point to another.
Quadrature amplitude modulation can be used with a variety of different formats:
8QAM, 16QAM, 64QAM, 128QAM, 256QAM
Basic knowledge of QAM modulator
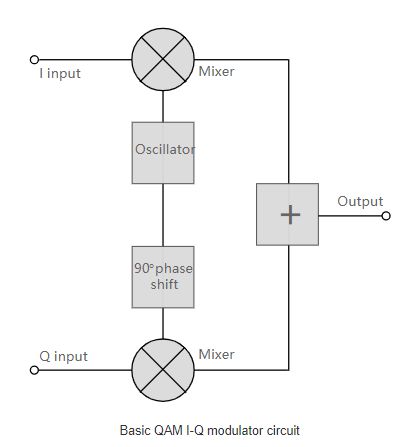
The QAM modulator essentially follows the idea that can be seen from the basic QAM theory, where there are two carrier signals and the phase shift between them is 90°. They are then amplitude modulated with two data streams called I or in-phase and Q or quadrature data streams. These are generated in the baseband processing area.A QAM modulator works like a translator, helping to translate digital packets into an analog signal to transfer data seamlessly.
The two synthesized signals are added together, then processed as needed in the RF signal chain. They are usually converted in frequency to the desired final frequency and amplified as needed.
QAM demodulator basics
The QAM demodulator is very much the reverse of the QAM modulator.The signals enter the system, they are split and each side is applied to a mixer. One half has the in-phase local oscillator applied and the other half has the quadrature oscillator signal applied.
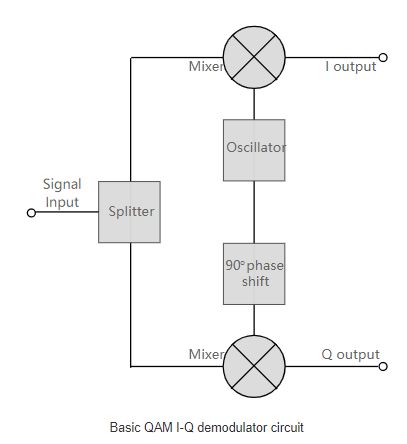
The basic modulator assumes that the two quadrature signals remain exactly in quadrature.A further requirement is to derive a local oscillator signal for the demodulation that is exactly on the required frequency for the signal. Any frequency offset will be a change in the phase of the local oscillator signal with respect to the two double sideband suppressed carrier constituents of the overall signal.
The system includes circuits for carrier recovery, usually phase-locked loops-some even have inner and outer loops. It is important to recover the phase of the carrier, otherwise the bit error rate of the data will be affected.
The circuit shown above shows common IQ QAM modulator and demodulator circuits used in a large number of different fields. These circuits are not only made of discrete components, but are more commonly used in integrated circuits that can provide a large number of functions.

