Products Category
- FM Transmitter
- 0-50w 50w-1000w 2kw-10kw 10kw+
- TV Transmitter
- 0-50w 50-1kw 2kw-10kw
- FM Antenna
- TV Antenna
- Antenna Accessory
- Cable Connector Power Splitter Dummy Load
- RF Transistor
- Power Supply
- Audio Equipments
- DTV Front End Equipment
- Link System
- STL system Microwave Link system
- FM Radio
- Power Meter
- Other Products
- Special for Coronavirus
Products Tags
Fmuser Sites
- es.fmuser.net
- it.fmuser.net
- fr.fmuser.net
- de.fmuser.net
- af.fmuser.net ->Afrikaans
- sq.fmuser.net ->Albanian
- ar.fmuser.net ->Arabic
- hy.fmuser.net ->Armenian
- az.fmuser.net ->Azerbaijani
- eu.fmuser.net ->Basque
- be.fmuser.net ->Belarusian
- bg.fmuser.net ->Bulgarian
- ca.fmuser.net ->Catalan
- zh-CN.fmuser.net ->Chinese (Simplified)
- zh-TW.fmuser.net ->Chinese (Traditional)
- hr.fmuser.net ->Croatian
- cs.fmuser.net ->Czech
- da.fmuser.net ->Danish
- nl.fmuser.net ->Dutch
- et.fmuser.net ->Estonian
- tl.fmuser.net ->Filipino
- fi.fmuser.net ->Finnish
- fr.fmuser.net ->French
- gl.fmuser.net ->Galician
- ka.fmuser.net ->Georgian
- de.fmuser.net ->German
- el.fmuser.net ->Greek
- ht.fmuser.net ->Haitian Creole
- iw.fmuser.net ->Hebrew
- hi.fmuser.net ->Hindi
- hu.fmuser.net ->Hungarian
- is.fmuser.net ->Icelandic
- id.fmuser.net ->Indonesian
- ga.fmuser.net ->Irish
- it.fmuser.net ->Italian
- ja.fmuser.net ->Japanese
- ko.fmuser.net ->Korean
- lv.fmuser.net ->Latvian
- lt.fmuser.net ->Lithuanian
- mk.fmuser.net ->Macedonian
- ms.fmuser.net ->Malay
- mt.fmuser.net ->Maltese
- no.fmuser.net ->Norwegian
- fa.fmuser.net ->Persian
- pl.fmuser.net ->Polish
- pt.fmuser.net ->Portuguese
- ro.fmuser.net ->Romanian
- ru.fmuser.net ->Russian
- sr.fmuser.net ->Serbian
- sk.fmuser.net ->Slovak
- sl.fmuser.net ->Slovenian
- es.fmuser.net ->Spanish
- sw.fmuser.net ->Swahili
- sv.fmuser.net ->Swedish
- th.fmuser.net ->Thai
- tr.fmuser.net ->Turkish
- uk.fmuser.net ->Ukrainian
- ur.fmuser.net ->Urdu
- vi.fmuser.net ->Vietnamese
- cy.fmuser.net ->Welsh
- yi.fmuser.net ->Yiddish
An Ultimate Guide to Potentiometer (POT)

For electronic engineers, in order to measure the unknown voltage, potentiometer will be utilized.
So, what is a potentiometer? What kinds of characteristics do potentiometers have? What is Construction of Potentiometer? And how do electronic engineers use potentiometers to measure the unknown voltage?
In this article, we will answer the above questions about potentiometers and then show you the basics of potentiometers.
If you are not clear about potentiometers, keep reading! If you find it useful, welcome to share or bookmark our content!
Content
● What Kinds of Characteristics do Potentiometers Have?
● What is Construction of Potentiometer?
● How does a Potentiometer Work?
● FAQ
Definition of Potentiometers
A Potentiometer is an application of a resistive transducer, which belongs to a kind of passive transducer. The instrument designs for measuring the unknown voltage by comparing it with the known voltage, such type of instrument is known as the potentiometer.
In other words, the potentiometer is the three terminal device used for measuring the potential differences by manually varying the resistances. The known voltage is drawn by the cell or any other supply sources.
The potentiometer uses the comparative method which is more accurate than the deflection method.
So, it is mostly used in the places where higher accuracy is required or where no current flows from the source under test.
The potentiometer, as an application of transducers, is used in the electronic circuit, especially for controlling the volume.
What Kinds of Characteristics do Potentiometers Have?

The following are the important characteristics of the potentiometer.
● Accurateness: As an example of a resistive transducer, the potentiometer is very accurate because its works on the comparing method rather than the deflection pointer method for determining the unknown voltages. It measures the null or balance point which does not require power for the measurement.
● Not interfered by source resistance: The working of the potentiometer is free from the source resistance because no current flows through the potentiometer when it is balanced.
What is Construction of Potentiometer?
The construction of the potentiometer is categorised into two parts. They are the sliding and non-sliding parts.
The sliding contact is a called wiper. The motion of the sliding contacts is either translatory or rotational.
Some potentiometer uses both the translatory and rotational motions. Such type of potentiometer uses the resistor in the form of a helix, and hence they are called heliports.
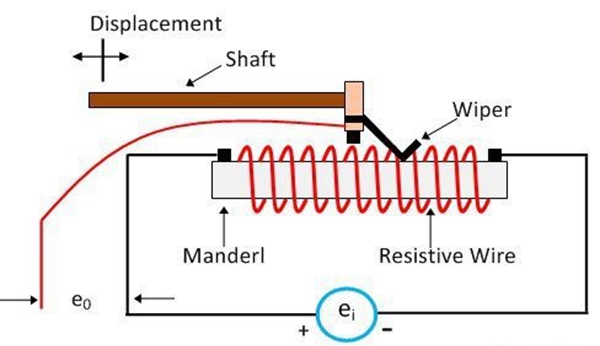
The potentiometer has three terminals, the two terminals are connected to the resistor, and the third terminal is connected to the wiper which is movable with the wire.
Because of this moving wire, the variable potential is tapped off. The third terminal is used for controlling the variable resistor.
The potential of the third terminal is controlled by changing the applying potential at the end of the resistor. The body of the potentiometer is made up of resistive material, and the wire is wound on it.
How does a Potentiometer Work?
The working principle of the potentiometer is explained through the circuit shown below. Consider S is the switch used for connecting or disconnecting the galvanometer from the potentiometer.
The battery through the rheostat and slide wire supply the working current. The working current may vary by changing the setting of the rheostat.
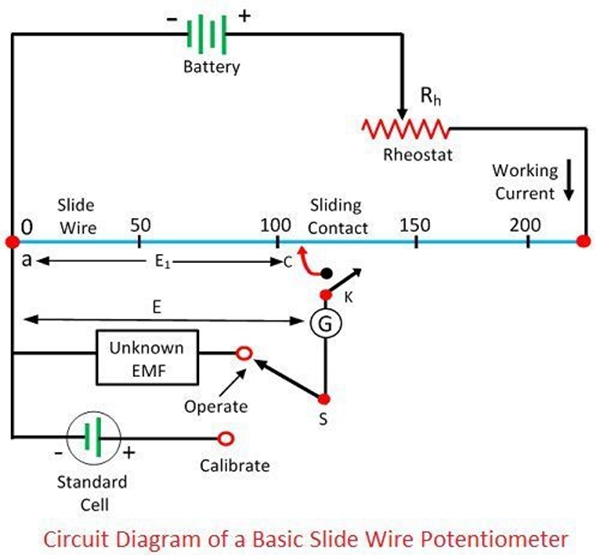
The method of findings the unknown voltage depends on the sliding position of the contact at which the galvanometer shows the zero deflection.
The zero or null deflection of galvanometer shows that the potential of the unknown source E and the voltage drops E1 across the sliding wires are equal.
Thus, the potential of the unknown voltage is evaluated by knowing the voltage drop across the ac portion of the sliding wire.
The slide wire has the uniform cross-section and resistance across the entire length. As the resistance of the sliding wire is known, then it is easily controlled by adjusting the working current.
The process of equalising the working voltage as that of voltage drop is known as the standardisation.
1. Q: What is Potentiometer and Its Types?
A: There are two main types of potentiometers, linear potentiometers and rotary potentiometers. Rotary and linear potentiometers are mechanically very similar, each consisting of two fixed terminals, a moving terminal (called a wiper), and a resistive rod (also called a track).
2. Q: Why Potentiometer is Used?
A: A potentiometer is a position sensor. They are used to measure displacement in any direction. In linear potentiometers, the track is straight, while in rotary potentiometers, the track is circular. The cursor moves along the track, and the displacement is measured by scaling the input voltage.
3. Q: What is Potentiometer and Its Working?
A: Potentiometers work by changing the position of the sliding contact across a uniform resistance. The two terminals of the potentiometer input source are fixed across the resistor. To adjust the output voltage, the sliding contact moves along the resistance on the output side.
4. Q: What do Potentiometers Measure?
A: A potentiometer works by comparing the voltage to be measured with a known voltage; it is used to measure very low voltages. Electronic voltmeters use amplification or rectification (or both) to measure AC or DC voltage.
5. Q: Are Potentiometers Polarized?
A: They are not polarized, so they can run in reverse. Potentiometers, on the other hand, are made of a resistive element (usually graphite) that forms an arc and a sliding or sliding contact that moves over the arc.
In this share, we know the definition, characteristics, construction and working of a potentiometer. To some extent, this blog helps electronic engineers to learn a brief introduction to a potentiometer and use it to measure the unknown voltage well.
After reading this blog, do you know more anout a potentiometer? Do you have any questions about a potentiometer? Leave a message below and share your ideas! If you think this share is helpful for you, don't forget to share this page!
Also Read
● How to Build Programmable Oscillators Using Digital Potentiometers
● How Potentiometer Works? Basics, Symbol, Applications, Taper
● How to Use a Rotary Potentiometer to Keep Your Office Neighbors Away

