Products Category
- FM Transmitter
- 0-50w 50w-1000w 2kw-10kw 10kw+
- TV Transmitter
- 0-50w 50-1kw 2kw-10kw
- FM Antenna
- TV Antenna
- Antenna Accessory
- Cable Connector Power Splitter Dummy Load
- RF Transistor
- Power Supply
- Audio Equipments
- DTV Front End Equipment
- Link System
- STL system Microwave Link system
- FM Radio
- Power Meter
- Other Products
- Special for Coronavirus
Products Tags
Fmuser Sites
- es.fmuser.net
- it.fmuser.net
- fr.fmuser.net
- de.fmuser.net
- af.fmuser.net ->Afrikaans
- sq.fmuser.net ->Albanian
- ar.fmuser.net ->Arabic
- hy.fmuser.net ->Armenian
- az.fmuser.net ->Azerbaijani
- eu.fmuser.net ->Basque
- be.fmuser.net ->Belarusian
- bg.fmuser.net ->Bulgarian
- ca.fmuser.net ->Catalan
- zh-CN.fmuser.net ->Chinese (Simplified)
- zh-TW.fmuser.net ->Chinese (Traditional)
- hr.fmuser.net ->Croatian
- cs.fmuser.net ->Czech
- da.fmuser.net ->Danish
- nl.fmuser.net ->Dutch
- et.fmuser.net ->Estonian
- tl.fmuser.net ->Filipino
- fi.fmuser.net ->Finnish
- fr.fmuser.net ->French
- gl.fmuser.net ->Galician
- ka.fmuser.net ->Georgian
- de.fmuser.net ->German
- el.fmuser.net ->Greek
- ht.fmuser.net ->Haitian Creole
- iw.fmuser.net ->Hebrew
- hi.fmuser.net ->Hindi
- hu.fmuser.net ->Hungarian
- is.fmuser.net ->Icelandic
- id.fmuser.net ->Indonesian
- ga.fmuser.net ->Irish
- it.fmuser.net ->Italian
- ja.fmuser.net ->Japanese
- ko.fmuser.net ->Korean
- lv.fmuser.net ->Latvian
- lt.fmuser.net ->Lithuanian
- mk.fmuser.net ->Macedonian
- ms.fmuser.net ->Malay
- mt.fmuser.net ->Maltese
- no.fmuser.net ->Norwegian
- fa.fmuser.net ->Persian
- pl.fmuser.net ->Polish
- pt.fmuser.net ->Portuguese
- ro.fmuser.net ->Romanian
- ru.fmuser.net ->Russian
- sr.fmuser.net ->Serbian
- sk.fmuser.net ->Slovak
- sl.fmuser.net ->Slovenian
- es.fmuser.net ->Spanish
- sw.fmuser.net ->Swahili
- sv.fmuser.net ->Swedish
- th.fmuser.net ->Thai
- tr.fmuser.net ->Turkish
- uk.fmuser.net ->Ukrainian
- ur.fmuser.net ->Urdu
- vi.fmuser.net ->Vietnamese
- cy.fmuser.net ->Welsh
- yi.fmuser.net ->Yiddish
What is Resistance? All You Need to Know

Resistance is one of the fundamental concepts in electricity and plays a key role in an electrical circuit. For electronic engineers and people who need to do with electricity and circuit, it is essential to have a comprehensive understanding of resistance.
So, here come some questions. Do you know what resistance is? How many types does resistance have? What is resistivity? What is series and parallel resistance in the circuit?
Now, this page offers basic knowledge about resistance, along with a detailed explanation of resistivity and series and parallel resistance in the circuit.
Let's begin the reading!
Content
● Series and Parallel Resistance in the Circuit
● FAQ
Resistance is the property of a material by virtue of which it opposes the flow of electrons through the material. It restricts the flow of the electron through the material. It is denoted by (R) and is measured in ohms (Ω).
The Basics Tutorial of Electrical Resistance, Resistors and Ohm's law
When the voltage is applied across the resistor the free electrons start accelerating. These moving electrons collide with each other and hence opposes the flow of electrons. The opposition of electrons is known as the resistance.
The heat is generated when the atom or molecules are colliding with each other. The resistance of any material depends on two factors: the shape of the material and material type (what material it is made up of).
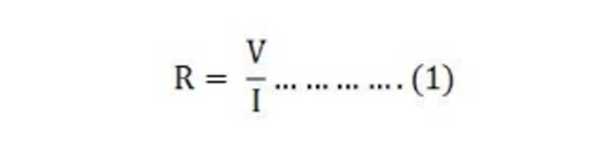
It is clear from the above equation (1) that resistance is directly proportional to the voltage and inversely proportional to the current of the circuit. It is also given below.
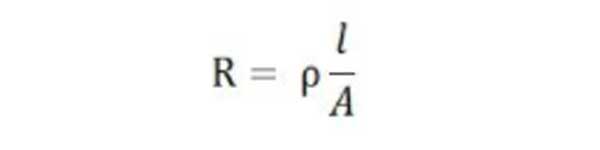
This formula also applies to the working priciple of a resistive transducer.
Where,
R is the resistance of any conductor or material measured in ohmsρ is the resistivity of the material and is measured in ohms meter
l is the length of the material or conductor in meters
A is the conductor’s cross-sectional area in meter square
Resistivity (ρ) is defined as the ability of the conductor or the material to oppose the electric current. The resistance of any conductor is measured by the instrument known as Ohmmeter.
The collision of atoms with the free electrons causes the heat to develop when an electric current flows through any conductor or material.
If a current of I ampere is passing through the conductor and the potential difference is V volts across the conductor, then the power absorbed by the resistor is given by the equation (3) shown below
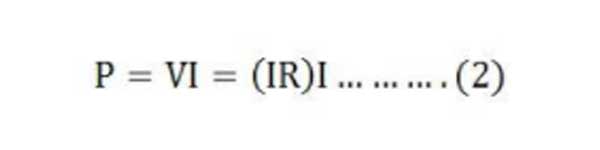
As we know V = IR

The energy lost in the resistance in the form of heat and is derived as
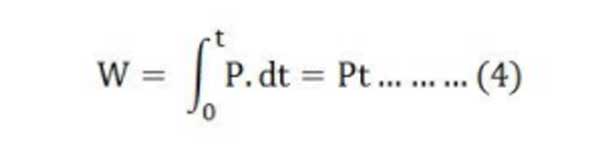
Putting the value of P from the equation (3) in equation (4) we will get
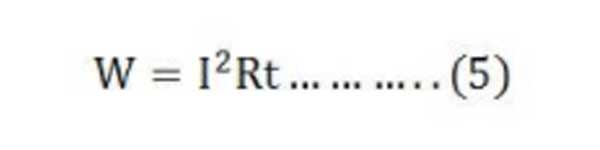
As we know I = V/R, hence putting the value of I in equation (5) we will get
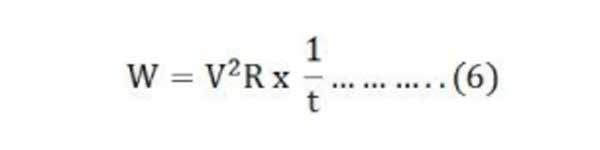
The above equation (6) shows the equation for energy loss in the form of heat.
● Static Resistance
It is similar to the normal resistance of the circuit given as R=V/I. It determines the power dissipation in an electric circuit. It is also defined as the slope of the line from the origin through various points on the curve.
● Differential Resistance
It is also known as the incremental or dynamic resistance of the circuit. It is the derivative of the ratio of voltage to the current. Differential resistance is given by the formula shown below
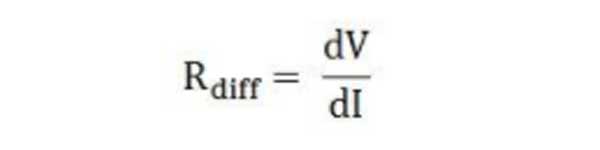
Most of electronic devices, including transducers, have many relationships and applications with resistance.
● Potentiometers, a types of variable resistors are used to manually change resistance in a circuit or measure the potential difference across a circuit.
● The resistive transducers is an electronic device that is capable of measuring various physical quantities like temperature, pressure, vibration, force, etc. Resistive transducers are available in various sizes and have a considerably high amount of resistance. The resistive transducer is a type of passive transducer.
Series and Parallel Resistance in the circuit
● Series Resistance Circuit
If the various resistances suppose R1, R2, R3 connected together in series as shown in the figure below is termed as a series resistance circuit.
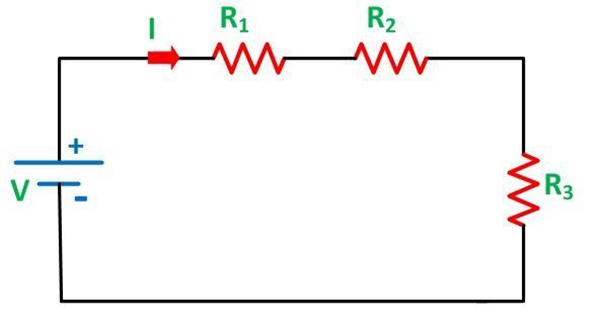
The equivalent or total resistance is given by the equation.
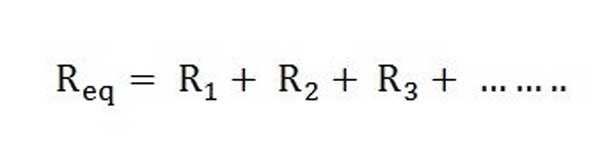
● Parallel Resistance Circuit
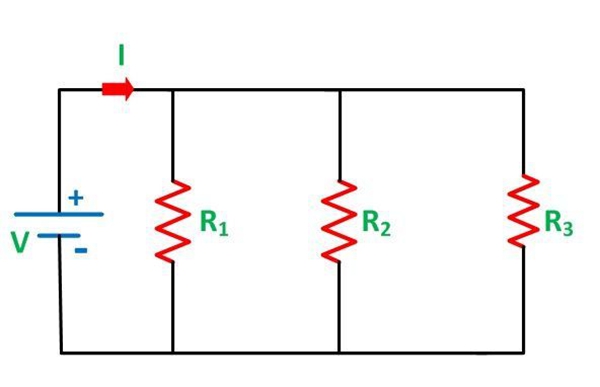
The various resistances suppose R1, R2, R3 are connected in parallel with each other as shown in the circuit below is known as Parallel Resistance Circuit.
The equivalent or total resistance is given by the equation.
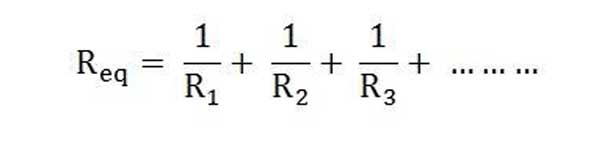
1. Q: What is the Resistance in Electricity?
A: Resistance (i.e. resistance) is a force that counteracts the flow of current. Resistance values are expressed in ohms (Ω). When there is an electronic difference between the two terminals, current flows from high to low. Resistance counteracts this flow.
2. Q: What is Resistance and Example?
A: Resistance is defined as refusal to budge or slow down or prevent something. An example of resistance is a child fighting her captive. An example of drag is wind blowing on the wings of an airplane.
3. Q: What Causes Resistance?
A: Electric current flows when electrons pass through a conductor, such as a wire. The moving electrons can collide with ions in the metal. This makes it harder for current to flow and creates resistance.
4. Q: What is Resistor and Resistance?
A: Resistance is the limitation of electron flow. Resistance is the opposite of current. Resistance is denoted by R in ohms (Ω). A resistor is a device designed to create electrical resistance. Resistors can be used to limit current, divide voltage, or generate heat.
In this share, we learn the definition and types of resistance, resistivity and series and parallel resistance in the circuit. Hope this article has helped you understand resistance better.
Feel free to leave a comment below if you have any ideas and questions about resistance. If this blog is helpful to you, don't forget to share this page!
Also Read
● What is Resistance Thermometer: Construction & Its Working
● Resistance and Impedance in an AC Circuit
● Resistance vs Impedance
