Products Category
- FM Transmitter
- 0-50w 50w-1000w 2kw-10kw 10kw+
- TV Transmitter
- 0-50w 50-1kw 2kw-10kw
- FM Antenna
- TV Antenna
- Antenna Accessory
- Cable Connector Power Splitter Dummy Load
- RF Transistor
- Power Supply
- Audio Equipments
- DTV Front End Equipment
- Link System
- STL system Microwave Link system
- FM Radio
- Power Meter
- Other Products
- Special for Coronavirus
Products Tags
Fmuser Sites
- es.fmuser.net
- it.fmuser.net
- fr.fmuser.net
- de.fmuser.net
- af.fmuser.net ->Afrikaans
- sq.fmuser.net ->Albanian
- ar.fmuser.net ->Arabic
- hy.fmuser.net ->Armenian
- az.fmuser.net ->Azerbaijani
- eu.fmuser.net ->Basque
- be.fmuser.net ->Belarusian
- bg.fmuser.net ->Bulgarian
- ca.fmuser.net ->Catalan
- zh-CN.fmuser.net ->Chinese (Simplified)
- zh-TW.fmuser.net ->Chinese (Traditional)
- hr.fmuser.net ->Croatian
- cs.fmuser.net ->Czech
- da.fmuser.net ->Danish
- nl.fmuser.net ->Dutch
- et.fmuser.net ->Estonian
- tl.fmuser.net ->Filipino
- fi.fmuser.net ->Finnish
- fr.fmuser.net ->French
- gl.fmuser.net ->Galician
- ka.fmuser.net ->Georgian
- de.fmuser.net ->German
- el.fmuser.net ->Greek
- ht.fmuser.net ->Haitian Creole
- iw.fmuser.net ->Hebrew
- hi.fmuser.net ->Hindi
- hu.fmuser.net ->Hungarian
- is.fmuser.net ->Icelandic
- id.fmuser.net ->Indonesian
- ga.fmuser.net ->Irish
- it.fmuser.net ->Italian
- ja.fmuser.net ->Japanese
- ko.fmuser.net ->Korean
- lv.fmuser.net ->Latvian
- lt.fmuser.net ->Lithuanian
- mk.fmuser.net ->Macedonian
- ms.fmuser.net ->Malay
- mt.fmuser.net ->Maltese
- no.fmuser.net ->Norwegian
- fa.fmuser.net ->Persian
- pl.fmuser.net ->Polish
- pt.fmuser.net ->Portuguese
- ro.fmuser.net ->Romanian
- ru.fmuser.net ->Russian
- sr.fmuser.net ->Serbian
- sk.fmuser.net ->Slovak
- sl.fmuser.net ->Slovenian
- es.fmuser.net ->Spanish
- sw.fmuser.net ->Swahili
- sv.fmuser.net ->Swedish
- th.fmuser.net ->Thai
- tr.fmuser.net ->Turkish
- uk.fmuser.net ->Ukrainian
- ur.fmuser.net ->Urdu
- vi.fmuser.net ->Vietnamese
- cy.fmuser.net ->Welsh
- yi.fmuser.net ->Yiddish
3 Main Types of Passive Transducers You Should Know about

A passive transducer is an electronic device that produces a change in some passive electrical quantity, for example, capacitance, resistance, or inductance.
Basically, a passive transducer needs extra electrical energy as the result of the stimulation.
However, if you're a transducer engineer, it is far not enough to know only by defining them in your daily work, to know the types, features, etc. of the passive transducers is also necessary.
On this page, 3 passive transducers, respectively resistive transducers, inductive transducers, and capacitive transducers, will be introduced from the perspective of what they exactly are and how they work.
Let's begin the learning!
Sharing is Caring!
Content
● What is a Resistive Transducer and How It Works?
● What is a Inductive Transducer and How It Works?
● What is a Capacitive Transducer and How It Works?
● FAQ
● Conclusion
What is a Resistive Transducer and How It Works?
A passive transducer is said to be a resistive transducer, when it produces the variation (change) in resistance value. The following formula for resistance, R of a metal conductor.
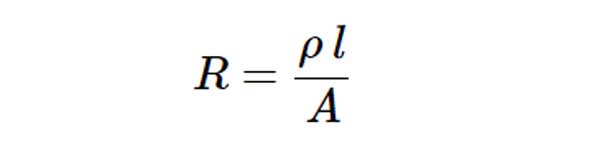
Where,
ρ is the resistivity of conductor
l is the length of conductor
Ais the cross sectional area of the conductor
Here comes the working principle of a resistive transducer. The resistance value depends on the three parameters ρ, l & A.
So, we can make the resistive transducers based on the variation in one of the three parameters ρ, l & A. The variation in any one of those three parameters changes the resistance value.
A Look at Working Principle of a Resistive Transducer
Resistance, R is directly proportional to the resistivity of conductor, ρ. So, as resistivity of conductor, ρ increases the value of resistance, R also increases.
Similarly, as resistivity of conductor, ρρ decreases the value of resistance, R also decreases.
Resistance, R is directly proportional to the length of conductor, l.
So, as length of conductor, l increases the value of resistance, R also increases. Similarly, as length of conductor, l decreases the value of resistance, R also decreases.
Resistance, R is inversely proportional to the cross sectional area of the conductor, A. So, as cross sectional area of the conductor, A increases the value of resistance, R decreases.
Similarly, as cross sectional area of the conductor, A decreases the value of resistance, R increases.
As to the examples of a resistive transducer, there are LDR (Light Dependent Resistor), Thermistor, LVDT (Linear Variable Differential Transformer), Potentiometer, Rheostat, Strain Gauge, etc.
What is a Inductive Transducer and How It Works?
A passive transducer is said to be an inductive transducer, when it produces the variation (change) in inductance value. The following formula for inductance, L of an inductor.

Equation 1
Where,
N is the number of turns of coil
S is the number of turns of coil
The following formula for reluctance, S of coil.
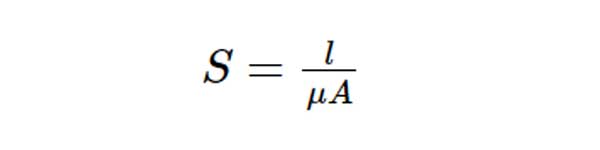
Equation 2
Where,
l is the length of magnetic circuit
μ is the permeability of core
A is the area of magnetic circuit through which flux flows
Substitute, Equation 2 in Equation 1.
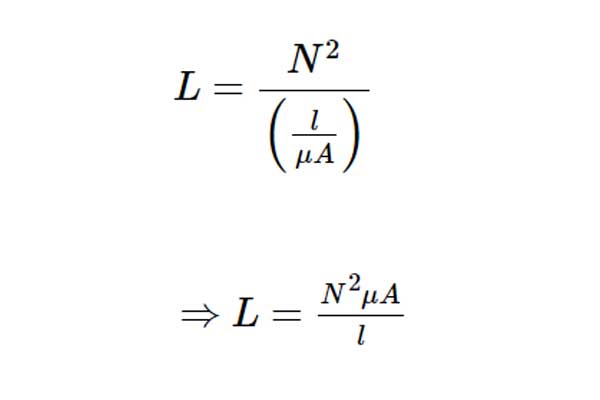
Equation 3
From Equation 1 & Equation 3, we can conclude that the inductance value depends on the three parameters N, S & μ.
So, we can make the inductive transducers based on the variation in one of the three parameters N, S & μ. Because, the variation in any one of those three parameters changes the inductance value.
Inductance, L is directly proportional to square of the number of turns of coil. So, as number of turns of coil, N increases the value of inductance, L also increases.
Similarly, as number of turns of coil, N decreases the value of inductance, L also decreases.
Inductance, L is inversely proportional to reluctance of coil, S. So, as reluctance of coil, S increases the value of inductance, L decreases.
Similarly, as reluctance of coil, S decreases the value of inductance, L increases.
Inductance, L is directly proportional to permeability of core, μ. So, as permeability of core, μμ increases the value of inductance, L also increases.
Similarly, as permeability of core, μ decreases the value of inductance, L also decreases.
What is a Capacitive Transducer and How It Works?
A passive transducer is said to be a capacitive transducer, one kind of transducer, when it produces the variation (change) in capacitance value. The following formula for capacitance, C of a parallel plate capacitor.
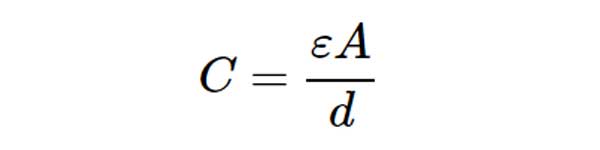
Where,
ε is the permittivity or the dielectric constant
A is the effective area of two plates
d is the effective area of two plates
The capacitance value depends on the three parameters ε, A & d. So, we can make the capacitive transducers based on the variation in one of the three parameters ε, A & d.
Because, the variation in any one of those three parameters changes the capacitance value.
Capacitance, C is directly proportional to permittivity, ε. So, as permittivity, εε increases the value of capacitance, C also increases.
Similarly, as permittivity, ε decreases the value of capacitance, C also decreases.
Capacitance, C is directly proportional to the effective area of two plates, A. So, as effective area of two plates, A increases the value of capacitance, C also increases.
Similarly, as effective area of two plates, A decreases the value of capacitance, C also decreases.
Capacitance, C is inversely proportional to the distance between two plates, d. So, as distance between two plates, d increases the value of capacitance, C decreases.
Similarly, as distance between two plates, d decreases the value of capacitance, C increases.
1. Q: How are Passive Transducers Classified?
A: Transducers can be roughly classified as i. Depends on the transduction format used as ii. primary and secondary transducers iii. components whose output energy is supplied solely by their input signal (the physical quantity being measured) are often referred to as "passive transducers".
2. Q: What are the Active and Passive Transducers?
A: Active transducers basically produce current or voltage as their output whereas passive transducers show changes in passive parameters as their output. Active transducers do not require an external power source, while passive transducers require an external energy source.
3. Q: What are Examples of Passive Transducer?
A: Some common examples of passive transducers are LDR (Light Dependent Resistor), Thermistor, LVDT (Linear Variable Differential Transformer), Potentiometer, Rheostat, Strain Gauge, etc.
4. Q: What are the Types of Transducer?
A: Current transducers.
Magnetic field transducers.
Pressure transducers.
A piezoelectric transducer.
Thermocouples.
An Electromechanical transducer.
Mutual induction transducers.
Strain gauges.
In this blog, we discussed about three main types of passive transducers that are resistive transducer, inductive transducer and capacitive transducer. To a large extent, this blog is useful for you to have a clear undersanding of these three types of transducers.
After reading this passage, do you have any other ideas about passive transducers? Leave a message below and share your ideas! And if you think this share is helpful for you, don't forget to share this page!
Also Read
● What are the differences between a sensor, transmitter, and transducer?
● Introduction to Sensors and Transducers
● What is a Transducer: Types & Its Ideal Characteristics

